Design and Analysis of Algorithm Lab 1 | Read Now
Design and Analysis of Algorithm Lab
Program 1:
- A] Create a Java class called Student with the following details as variables within it.
- USN
- Name
- Branch
- Phone
Write a Java Program to create n student objects and print the USN, Name, Branch, Phone of all these objects with the suitable headings
- B] Write a Java Program to implement the stack using arrays. Write Push(), Pop(), and Display() methods to demonstrate its working.
1a – Program Code
class student
{
String USN,NAME,BRANCH,PH;
student(String U,String N,String b,String p)
{
this.USN=U;
this.NAME=N;
this.BRANCH=b;
this.PH=p;
}
void display()
{
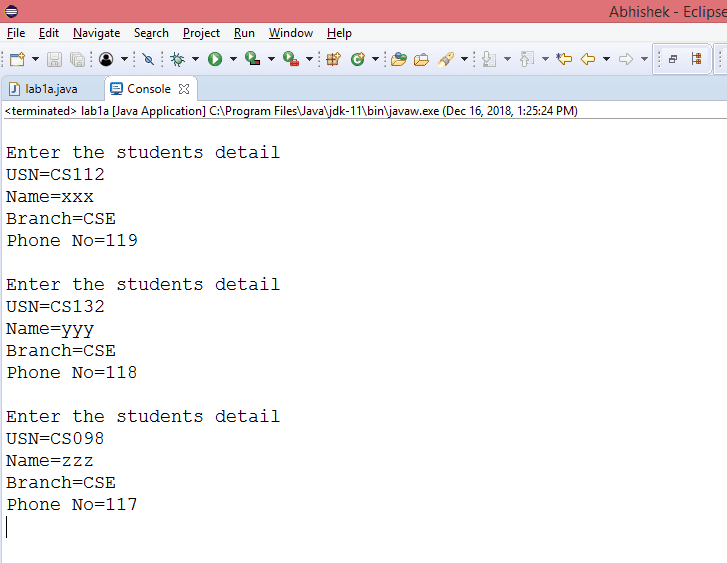
System.out.println("\nEnter the students detail");
System.out.println("USN="+this.USN);
System.out.println("Name="+this.NAME);
System.out.println("Branch="+this.BRANCH);
System.out.println("Phone No="+this.PH);
}
}
public class lab1a
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
student ob1=new student("CS112","xxx","CSE","119");
student ob2=new student("CS132","yyy","CSE","118");
student ob3=new student("CS098","zzz","CSE","117");
ob1.display();
ob2.display();
ob3.display();
}
}
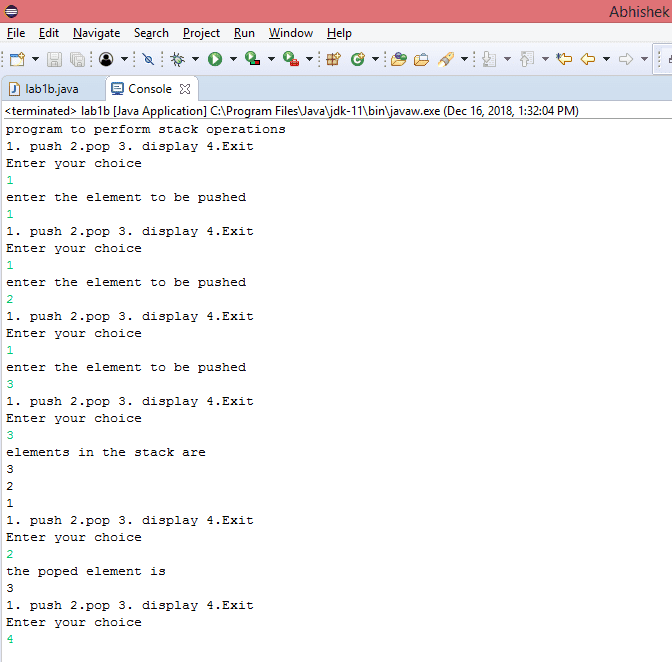
Output
1b – Program Code
import java.util.Scanner;
public class lab1b
{
final int max=5;
int s[]=new int[max];
int top=-1;
void push(int ele)
{
if(top>=max-1)
System.out.println("stack overflow");
else
s[++top]=ele;
}
int pop()
{
int z=0;
if(top==-1)
System.out.println("stack underflow");
else
z=s[top--];
return z;
}
void display()
{
if(top==-1)
System.out.println("stack empty");
else
{
for(int i=top;i>-1;i--)
System.out.println(s[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int q=1;
lab1b m = new lab1b();
System.out.println("program to perform stack operations");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(q!=0)
{
System.out.println("1. push 2.pop 3. display 4.Exit");
System.out.println("Enter your choice");
int ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
System.out.println("enter the element to be pushed");
int ele=sc.nextInt();
m.push(ele);
break;
case 2:
int popele;
popele=m.pop();
System.out.println("the poped element is");
System.out.println(popele+" ");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("elements in the stack are");
m.display();
break;
case 4:
q=0;
}
}
}
}
Output